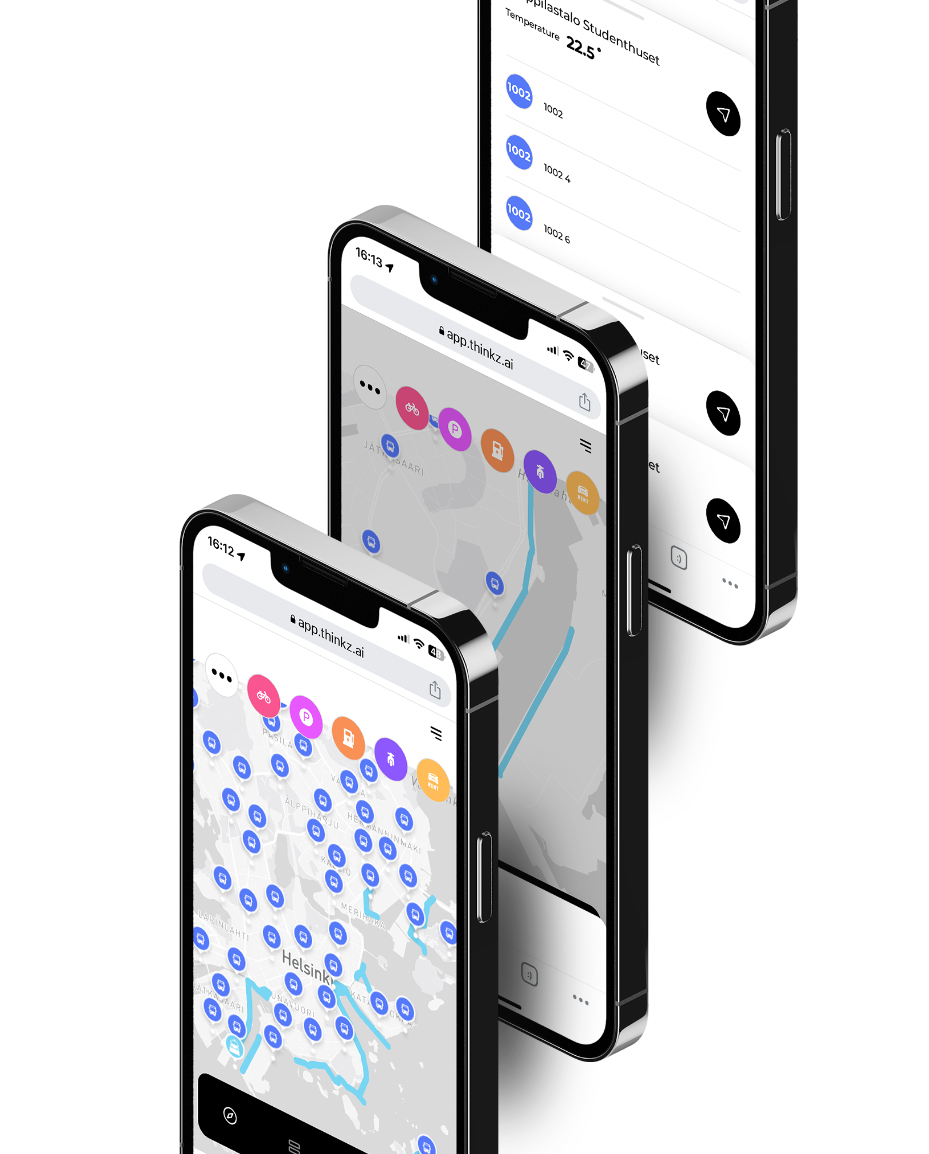
Join Thinkz & Bable Real-Time City Map IoT service Contest!
An Opportunity to Transform Your City with Real-Time IoT Data
Experience the Power of Real-Time presence: Get your city’s map animated in real time.
Choose Thinkz Real-Time services: The winner will have the opportunity to select one real-time service from our extensive list of available offerings.
IoT Integration on Thinkz Real-Time Map: We will integrate the city’s IoT data into our real-time map, bringing the chosen service to life.
Free Access for Citizens: The city’s inhabitants will enjoy free access to a dynamic, real-time map of the chosen service, fostering a smarter and more connected community.

Thinkz & Bable Contest – Smart City Real Time Map

Thinkz at Smart City Expo Barcelona 2025 – Meet Us at the French Pavilion, Booth E70
For the third year in a row, Thinkz is heading to the Smart City Expo World Congress in Barcelona (4–6 Nov). This global event brings together the world’s most innovative cities, integrators, and technology providers to shape the future of urban living.
We’re proud to be part of the French Pavilion (Booth E70), where we’ll showcase how real-time intelligence helps cities cut emissions, ease congestion, and improve daily life for both citizens and visitors.
📅 Plan your visit now. Secure a 20-minute slot with our team to explore your 2026 priorities and discover how Thinkz can help.
👉 Book a meeting with Thinkz at SCEWC
Thinkz we did
Use cases that are already leveraging
the Power of Real-Time Data





 REAL-TIME Digital Twin Mobility – Helsinki city
REAL-TIME Digital Twin Mobility – Helsinki city
Revolutionizing Helsinki’s Snow Plow System with Digital Twin Technology
Insights:
The residents and transportation services in the snowy city of Helsinki require up-to-date information on which roads have been cleared of snow in real-time. This information is crucial in helping them plan their journeys more safely and efficiently, whether it be choosing their route or determining if public transportation is an option.
Problem:
Residents of snowy cities require real-time updates on which roads have been cleared of snow to plan their journeys more safely and efficiently.
Solutions:
Real-time snowplow mapping uses intelligent technologies and mapping software to track and display snowplow locations and progress. By harnessing the power of IoTs on the city’s snow plows and other connected devices, the collected data can be transformed into real-time information and displayed on a live map.
The solution also includes multiple layers of information, connecting the snow-cleared route map to the city’s public and private transportation systems. The revolutionary pattern pending LDV technology by Thinkz ensures the accuracy of the data by connecting and verifying multiple sources of IoT data in real-time.
Digital Twins technology allows the solution to connect other IoT devices in the city, providing data from multiple sources in real-time. This data is transformed into a single, verified information source through the revolutionary pattern pending LDV technology by Thinkz.
Advantages:
Real-time snowplow mapping offers many benefits for the citizens :
Real-time road condition updates:
Enhances driver safety and informs route decisions.
Travel planning made easy:
Residents can plan trips and errands based on cleared roads.
Avoid uncleared roads:
Real-time mapping helps minimize travel time and reach destinations faster.
Informed route choices:
Reduces accident risk and improves overall road safety.
Current road status information:
Alleviates concerns and promotes peace of mind for residents.
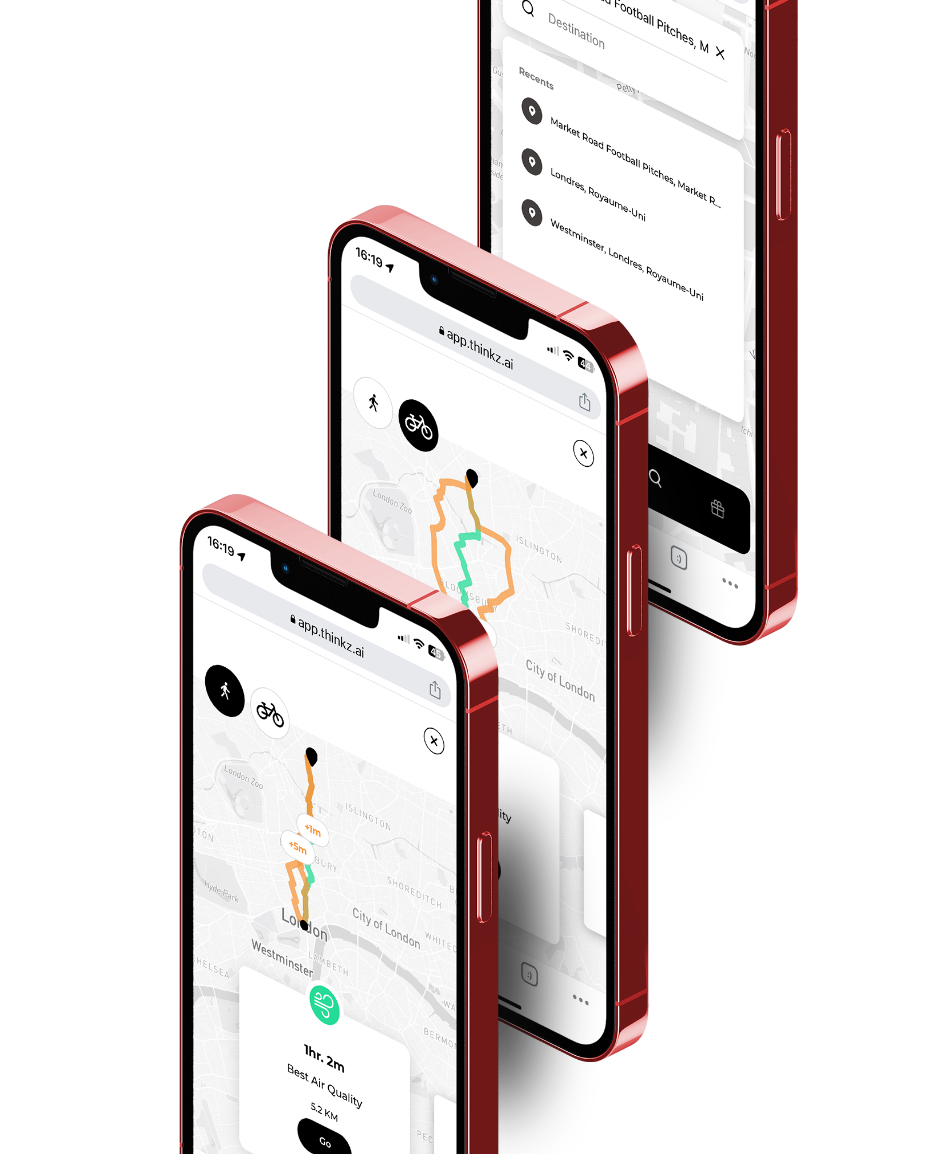
 Real-Time Air quality & Mobility – Westminster London City Hall
Real-Time Air quality & Mobility – Westminster London City Hall
Dynamic Clean-Air Routing: Utilizing IoT for Sustainable Living & Urban Mobility
Insights:
Access to real-time air quality data is essential for citizens to make informed decisions about their daily activities, leading to a healthier and more sustainable environment for all.
Problem:
Isolation of IoT devices due to cyber protection and privacy concerns prevents citizens from accessing air quality information. The challenge is to create a global network of IoT devices to provide free access to real-time air quality data in urban areas.
Solutions:
Collaboration between IoT devices provides boundless possibilities for enhancing urban living. Our innovative technology assimilates data from a variety of IoT devices, including CO2 sensors, to offer citizens real-time maps detailing the quickest and cleanest walking or cycling routes to their destinations.
This GDPR-compliant solution also delivers crucial information such as travel duration, air pollution levels, and street capacity.
The revolutionary pattern pending LDV technology by Thinkz ensures the accuracy of the data by connecting and verifying multiple sources of IoT data in real-time.
We are not data aggregators: All your data stays within your system. Further, we don’t collect or store data from end users and IOT devices.
Advantages:
Since DECEMBER 2022- Westminister’s citizens get access to cleaner air routes
Real-time air quality insights
enable informed decision-making for citizens’ daily activities, promoting healthier and more sustainable lifestyles.
Breaks the barriers of IoT device isolation
by harmonizing data from diverse IoT devices, including CO2 sensors and pedestal route.
Providing real-time maps
presenting the fastest and cleanest routes to citizens’ destinations.
Enhancing daily commuting experiences,
fostering more efficient and sustainable urban living.
Citizens can use Thinkz’s user-friendly real-time map to view all relevant air quality data on their route, empowering them to make informed decisions about their daily activities.
 Real-Time Mobility – Tel Aviv
Real-Time Mobility – Tel Aviv
Dynamic Clean-Air Routing: Utilizing IoT for Sustainable Living & Urban Mobility
Insights:
Tel Aviv, known for its vibrant life and bustling streets, offers an extensive range of micromobility options. Despite this, these options are spread across numerous apps, creating a disjointed experience for residents who cannot access real-time, consolidated information
Problem:
How to provide city residents with comprehensive, real-time information on all available public transportation options?
This requires the integration of unused data from multiple IoT devices, each with different owners and protocols, and the establishment of a machine-learning Live data verification to ensure data accuracy.
Solutions:
Thinkz addresses this issue with a unified platform providing real-time insights into all available micromobility options, including scooters and electronic rentals. This easily navigable, interactive real-time map is accessible on both mobile and desktop interfaces. It includes real-time information on available e-scooters, e-bikes, and other relevant public transportation options.
Our GDPR-compliant solution delivers vital information such as the availability and battery level of e-scooters and e-bikes, helping users make informed choices.
With Thinkz’s groundbreaking LDV technology, we ensure data accuracy by connecting and verifying multiple real-time IoT data sources.
Your data security is our priority. We don’t aggregate data; all your data stays within your system. Additionally, we don’t collect or store data from end users and IoT devices.
Advantages:
Since September 2022, Tel Aviv residents have been reaping the benefits of the Mobility 360° platform
Enhanced Convenience
Provides real-time information on the availability and location of e-scooters, e-bikes, and public transportation, simplifying planning and reducing search times.
Improved Mobility
With real-time updates on diverse transport modes, residents can make informed decisions to efficiently reach their destinations.
Sustainability Promotion
By providing real-time data on e-scooters and e-bikes, Thinkz’s platform promotes eco-friendly transportation.
Time Efficiency
Instant visibility of available transport modes reduces travel and waiting times.
Boosts Public Transport Usage
Real-time updates on public transportation schedules can motivate more residents to use these services, reducing congestion and carbon emissions.
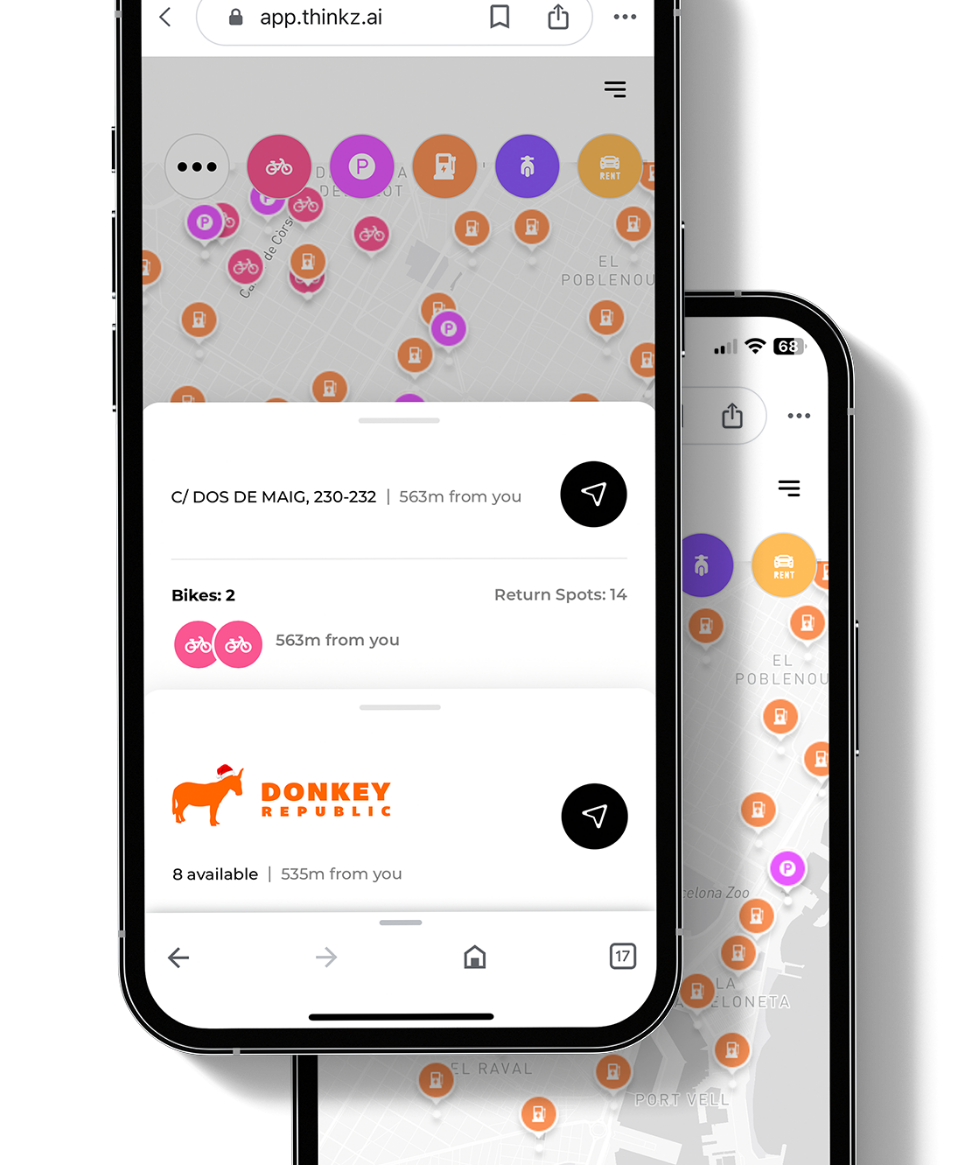
 Real-Time Mobility 360° – Barcelona
Real-Time Mobility 360° – Barcelona
Streamlining Urban Transport for Barcelona’s Residents through Mobility 360°
Insights:
While the city of Barcelona offers an array of options for optimizing urban mobility, these solutions are scattered across multiple applications. This fragmentation prevents residents from having a centralized and comprehensive overview of real-time mobility solutions.
Problem:
How to create a unified platform that provides city residents with comprehensive, real-time information on all available mobility options.
Solutions:
Thinkz addresses this challenge by presenting a centralized, real-time view of various mobility options, including micro-mobility devices such as scooters and bikes, along with real-time information for drivers such as available parking spots and EV charging stations. This solution manifests in a multi-layered, interactive, real-time map that’s intuitive to use on both mobile and desktop interfaces.
Our GDPR-compliant solution also provides vital details such as scooter and bike battery levels, the availability of return spots, and the number of available parking spaces.
Live Data Verification (LDV): Thinkz’s innovative and patent-pending LDV technology ensures data accuracy by verifying and connecting multiple sources of IoT data in real-time.
At Thinkz, we prioritize your data security: we do not aggregate data, and all your data remains within your system. Furthermore, we do not collect or store data from end users or IoT devices.
Advantages:
Since September 2022, Barcelona’s residents have benefitted from the Mobility 360° platform:
Enhanced Convenience
Provides real-time information on the availability and location of e-scooters, e-bikes, and public transportation, simplifying planning and reducing search times.
Improved Mobility
With real-time updates on diverse transport modes, residents can make informed decisions to efficiently reach their destinations.
Sustainability Promotion
By providing real-time data on e-scooters and e-bikes, Thinkz’s platform promotes eco-friendly transportation.
Time Efficiency
Instant visibility of available transport modes reduces travel and waiting times.
Boosts Public Transport Usage
Real-time updates on public transportation schedules can motivate more residents to use these services, reducing congestion and carbon emissions.
 Real-Time Mobility 360° – Berlin
Real-Time Mobility 360° – Berlin
Simplifying Urban Transport for Berlin and Its Surrounding Areas Through Mobility 360°
Insights:
Berlin, a bustling city with a diverse range of mobility solutions, faces a similar challenge to Barcelona. The myriad of car rental options available to residents and visitors alike are spread across various platforms, making it hard to get a holistic, real-time view of mobility choices.
Problem:
How to Develop a unified platform to provide real-time, comprehensive information on all available real-time transportation options and car rental options in the city.
Solutions:
Thinkz has stepped in to resolve this issue by offering a centralized, real-time view of car rental options available across Berlin. Our interactive, real-time map is accessible through both mobile and desktop interfaces and provides a multi-layered view of real-time mobility solutions including available rental cars, parking spaces, and EV charging stations.
Our solution adheres to GDPR guidelines, offering critical details such as the availability of rental cars, the number of return spots, and the number of available parking spaces.
With Thinkz’s patent-pending LDV technology, we ensure the accuracy of the data by connecting and verifying multiple IoT data sources in real time.
At Thinkz, data security is paramount. We are not data aggregators, all your data stays within your system. Plus, we don’t collect or store data from end users and IoT devices.
Advantages:
Since September 2022, residents and visitors of Berlin and its surrounding areas have enjoyed the benefits of the Mobility 360° platform:
Enhanced Convenience
Provides real-time information on the availability and location of e-scooters, e-bikes, and public transportation, simplifying planning and reducing search times.
Improved Mobility
With real-time updates on diverse transport modes, residents can make informed decisions to efficiently reach their destinations.
Sustainability Promotion
By providing real-time data on e-scooters and e-bikes, Thinkz’s platform promotes eco-friendly transportation.
Time Efficiency
Instant visibility of available transport modes reduces travel and waiting times.
Boosts Public Transport Usage
Real-time updates on public transportation schedules can motivate more residents to use these services, reducing congestion and carbon emissions.